INTRODUCTION
Nerve root fibrosis (NRF) represents a frequent postoperative sequela following spinal decompression, characterized by fibroblast invasion and scar formation around the dura mater. This fibrotic adhesion contributes to persistent pain and neurologic symptoms, often necessitating complex revision surgery with uncertain outcomes.1,2 Postoperative symptoms associated with adhesion and fibrosis affect about 15% of patients who underwent laminectomies.3,4 This condition may lead to persistent pain and neurological symptoms, and revision surgery for symptomatic fibrosis remains technically challenging with unpredictable outcomes.2,3 Consequently, strategies aimed at preventing postoperative adhesion have become an important area of investigation in spine surgery.2,3
To minimize adhesion formation, several anti-adhesive strategies have been developed, including the application of barrier materials that physically separate neural elements from postoperative hematoma and surrounding tissues.5,6 Among these materials, thermosensitive hydrogels composed of poloxamer and hyaluronic acid (HA) have received increasing attention.2,3,5–9 Poloxamer is a biocompatible, thermoresponsive triblock copolymer that transforms from a liquid to a gel at body temperature, allowing easy intraoperative application and prolonged retention at the surgical site.2,3,6–8 Hyaluronic acid (HA), a naturally occurring glycosaminoglycan, possesses viscoelastic, hydrating, and anti-inflammatory properties that support tissue healing and inhibit fibroblast migration.10–15 The combination of poloxamer and HA enhances gel stability, improves tissue adherence, and provides synergistic anti-adhesive effects, making it a promising biomaterial for epidural fibrosis prevention. To attain adequate anti-adhesion effects, this mechanical barrier should ideally remain for a specified duration between the dura and the adjacent tissues. An optimal anti-adhesive would be a thermo-sensitive sol-gel system that is available as a liquid at room temperature and transitions to a gel state in vivo. The swift transition from solution to gel facilitates easy injection of the agent, ensuring comprehensive coverage of the neural structure while minimizing drainage risk due to increased viscosity and extended residence time. Furthermore, additional hemostasis may be attained through tamponade effects from mild force during the gelation process.2,3
Bibliometric analysis provides a quantitative approach to evaluating scientific progress by mapping publication trends, citation patterns, and collaborative networks within a specific research field. It identifies influential authors, institutions, and journals, while revealing thematic evolution and emerging hotspots that may not be evident through conventional narrative reviews. Although numerous experimental and preclinical studies have investigated the efficacy of poloxamer and hyaluronic acid in reducing epidural fibrosis, no comprehensive bibliometric study has yet summarized global research activity, collaboration patterns, or emerging trends in this area. Existing literature primarily focuses on biological mechanisms or experimental outcomes, leaving a gap in understanding the broader scientific landscape and development trajectory of this topic.
Therefore, the present study aims to conduct a systematic bibliometric analysis to map global publications, identify key contributors, visualize co-authorship and keyword networks, and highlight emerging research hotspots related to the use of poloxamer and hyaluronic acid for the prevention of nerve root fibrosis following laminectomy. This analysis is intended to provide a macroscopic overview of research development and guide future investigations in this growing area of spinal surgery.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Data Source and Search Strategy
All bibliometric data were retrieved from the Web of Science Core Collection (WoSCC) database, including the Science Citation Index Expanded (SCIE) and Social Sciences Citation Index (SSCI). To ensure consistency and avoid database updates during analysis, all data were collected on March 26, 2025. Only articles and review articles published in English between January 1, 2000, and December 31, 2024, were included.
The following search query was applied to the WoSCC advanced search field:
TS = (“Biodegradable Hydrogel” OR “Poloxamer” OR “Hyaluronic Acid” OR “Hyaluronan” OR “Gelatin” OR “Hydrogel” OR “HA” OR “Copolymer” OR “Kolliphor” OR “Guardix”) AND TS = (“Epidural Fibrosis” OR “Postoperative Adhesion”) AND TS = (“Spinal Surgery” OR “Laminectomy” OR “Corpectomy”)
This query was designed to capture studies investigating the use of hydrogel-based biomaterials, particularly poloxamer and hyaluronic acid, in preventing postoperative epidural fibrosis and adhesion following spinal surgery.
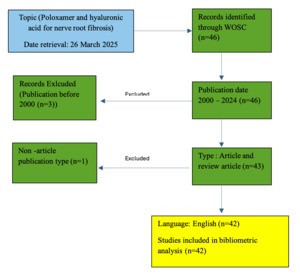
The study selection process is summarized in a flow diagram illustrating record identification, screening, exclusion, and final inclusion (Figure 1).
Eligibility Criteria
Inclusion criteria
-
Peer-reviewed articles and review articles.
-
Publications written in English.
-
Studies related to poloxamer, hyaluronic acid, or hydrogel-based materials for nerve root fibrosis or epidural adhesion prevention.
-
Publication period between 2000 and 2024.
Exclusion criteria
-
Non-English publications.
-
Conference abstracts, editorials, letters, or notes.
-
Articles published before 2000 4. Papers not directly addressing NRF or postoperative adhesion.
Data analysis and network mapping
Bibliographic data, including publication year, authorship, country of origin, citations, and keywords, were exported in plain text format. Bibliometric analyses were performed using VOSviewer (version 1.6.18) and Microsoft Excel to evaluate co-authorship networks, co-citation relationships, and keyword co-occurrence patterns in accordance with established bibliometric methodologies for medical literature analysis.
The screening process was conducted manually by three independent investigators (R.E., G.I., and J.S.). Disagreements were resolved by consensus, with final decisions made by the senior author (R.E.).
The bibliometric workflow and analytical framework employed in this study were conducted in accordance with established methodologies for medical bibliometric research. The study design, database selection, keyword strategy, data extraction, and network visualization using VOSviewer followed the standardized step-by-step approach described by Ganti et al., which outlines best practices for citation analysis, co-authorship mapping, co-citation analysis, and keyword co-occurrence visualization in medical literature.
Ethical statement
This study involved a systematic search and gathering of widely accessible literature data from WOSCC and did not include neither human nor animal subjects. As a result, the use of this data did not present any ethical issues and was exempt from needing ethics committee clearance.
RESULTS
Global publication trends on an annual basis
Initially, the researchers first reviewed 46 papers concerning the administration of poloxamer and HA for prevention of NRF and adhesion, ultimately included 42 studies with pre-determined criteria. Figure 2. illustrates the yearly increase trend in publishing yield. Publication output demonstrated a gradual increase over the study period, with a marked rise after 2010 and sustained activity in recent years. Approximately one-third of all included studies were published within the last five years, indicating growing research interest in the application of poloxamer and HA for NRF prevention.
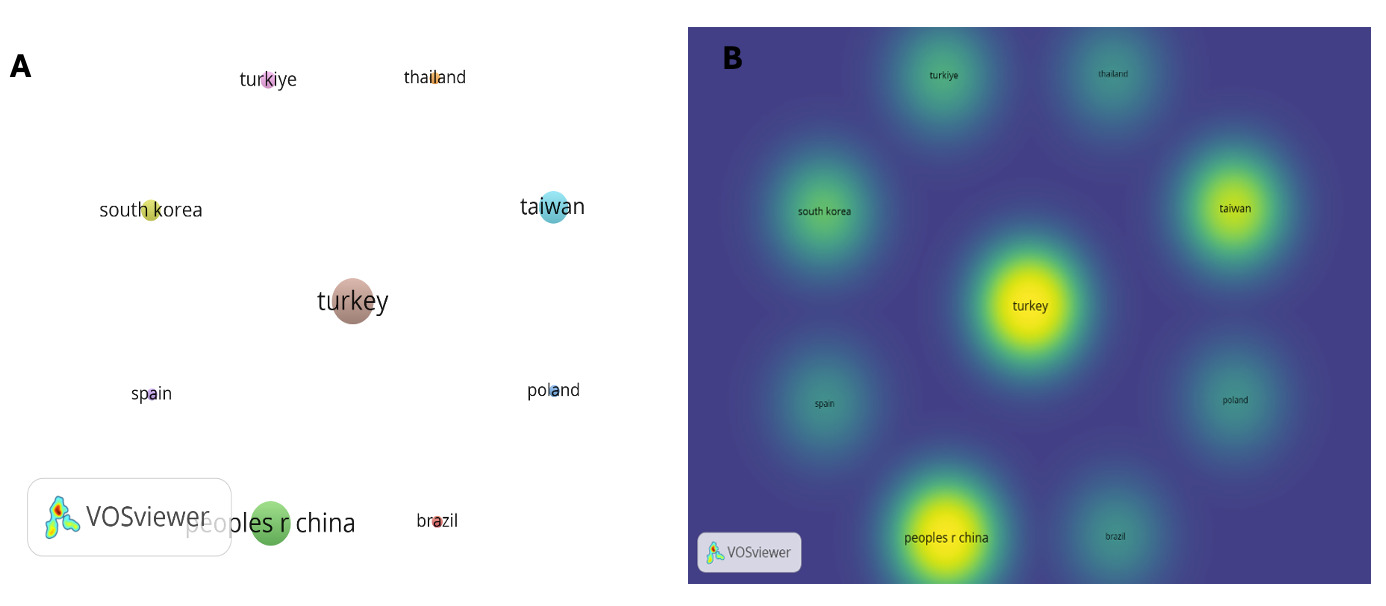
Distribution by country and number of citations
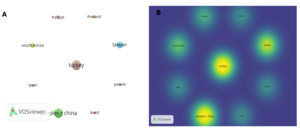
Research outputs of the most significant countries were displayed in Table 1.. Turkey was the most productive country, with a total of 16 publications (37.1%). China, Taiwan, South Korea, were all ranked below, with 13 publications (30.2%), 7 publications (16.3%), and 3 publications (7.7%), respectively. Out of 10 countries that contributed only 4 countries (40%) that contributed more than one research While Turkey produced the highest number of publications, China demonstrated greater citation impact, suggesting a higher influence of its research output. Figure 3 shows nternational collaboration between countries was limited.While the lines linking the circles show the degree of cooperation across the nations, the size of the circle in Figure 3A denotes the number of published papers in every nation. Figure 3B presents a country density map.
Authors and co-cited authors analysis
From 2000 to 2024, a total of 232 authors published 43 articles related to poloxamer and HA for the prevention of NRF. Among the top productive authors, we could find the most productive authors are Emre I tied with Emrah K, Mei-Hsiu C, Ming-Hong C, Cheng-Yi L, Tse-Ying L, and Jui-Sheng S, who published 3 papers. Authorship analysis revealed a specific network of collaboration among various authors. For example, Emre I and Emrah K collaborated closely (Figure 4A). authors who are cited together in one or more publications are termed co-cited authors. Co-citation links are established among these authors. Mei-Hsu C was the most often mentioned author, with 70 co-citations, followed by Yu S with 67 co-citations, and Emre I with 54 co-citations, as depicted in Figure 4B. A total of 1,199 co-cited writers were incorporated
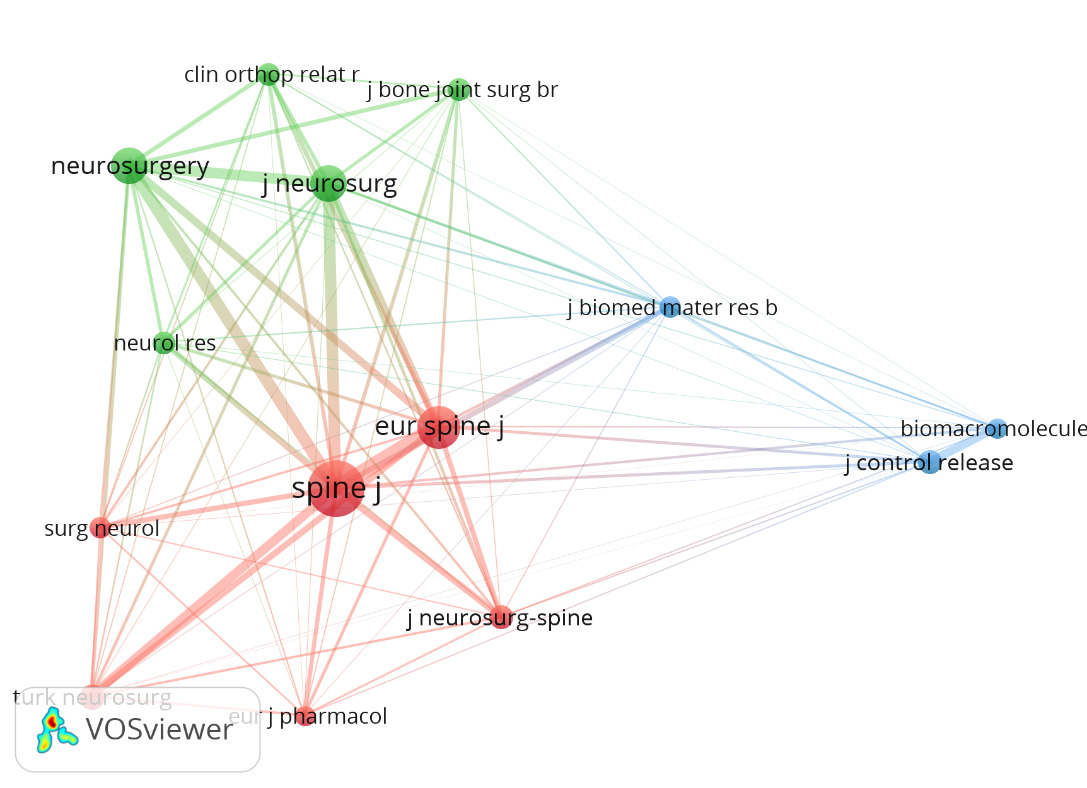
Journal distribution and co-citation analysis
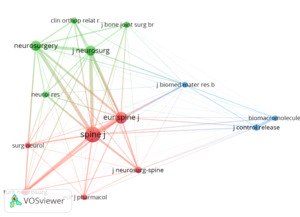
A total of 34 academic journals have published 43 articles concerning the use of poloxamer and HA in the prevention of NRF and adhesion from 2000 to 2024. Table 2 provides a summary of the ten journals with the highest activity, each having at least two publications. Our analysis revealed that Acta Orthopedica et Traumatologica Turcica had the highest publication count, with three articles, while several other journals shared the second position. The Journal of Orthopedic Surgery and Research stands out among active academic journals, recording the highest impact factor at 2.8. The influence of journals is assessed through the frequency of co-citations, indicating the journal’s significance within a specific research domain is demonstrated in Figure 5. Consequently, we conducted a co-citation analysis involving 34 journals. The journals that received the most citations include the Journal of Neuro Surgery - Spine with 87 co-citations, followed by the Euro Spine Journal with 58 co-citations, and the Neuro Surgery Journal with 55 co-citations.
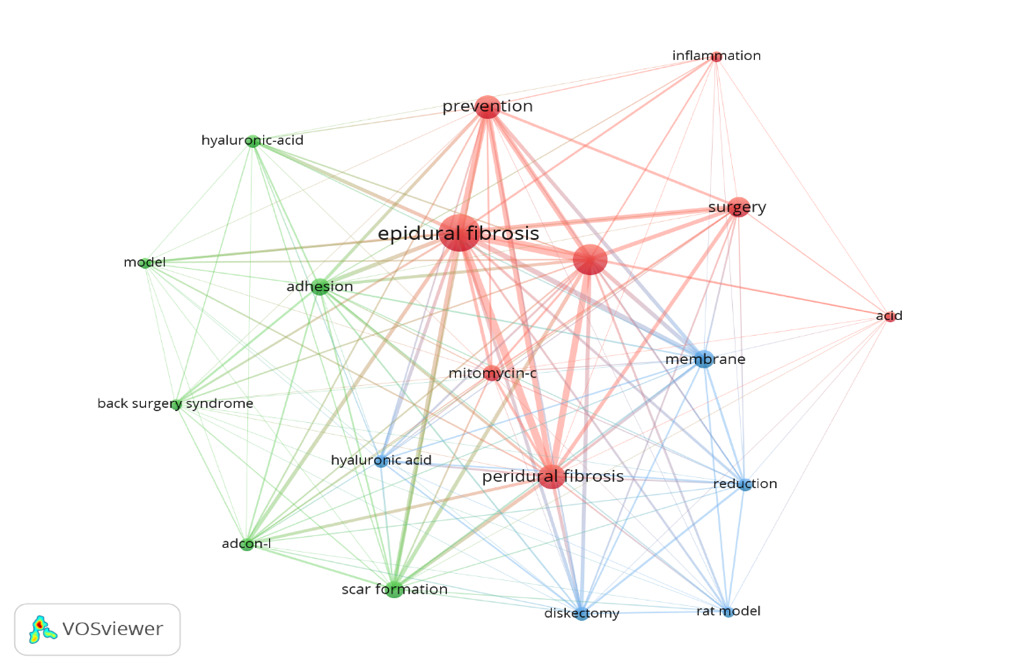
Keyword co-occurrence analysis
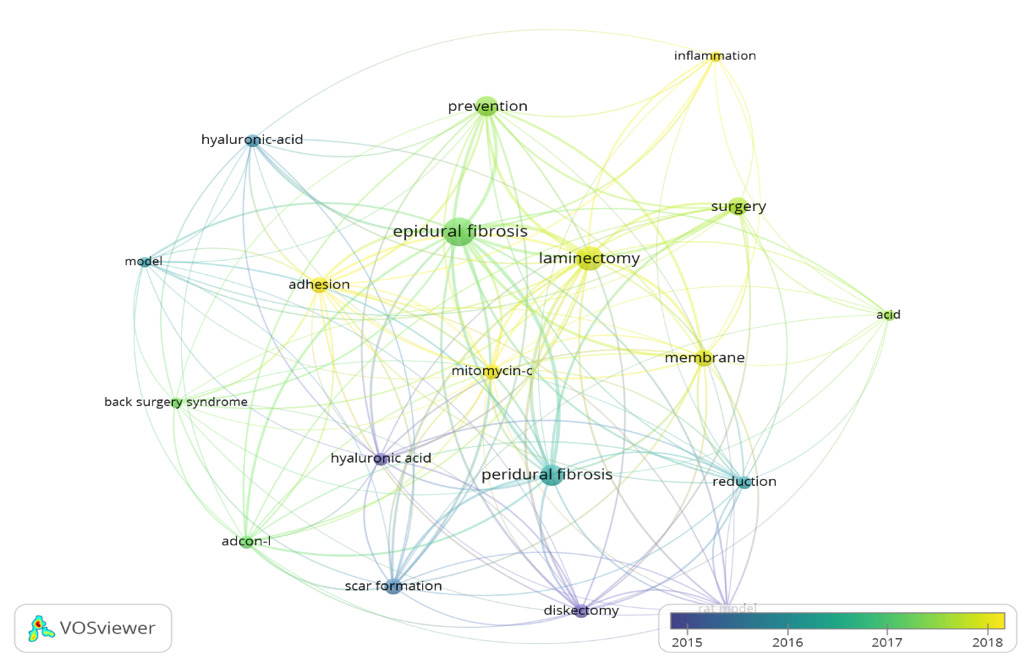
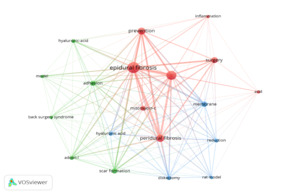
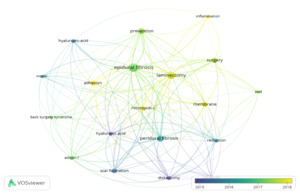
The investigation of trending and cutting-edge terminology constitutes the essence of the published paper, enabling us to summarize research focal points and identify prominent subjects within a specific domain. Keywords, as a crucial component of an article, delineate the primary subject of the piece. Consequently, we examined the keywords of the published research and constructed the network maps utilizing VOSviewer software. This study gathered and analyzed a total of 274 keywords. Figure 6 illustrates that 19 keywords emerged in the image, identified as those applied more than five times. The most often occurring keywords were “epidural fibrosis” (32), “laminectomy” (24), “peridural fibrosis” (17), “prevention” (16), “surgery” (13), “membrane” (11), “adhesion” (10), and “scar formation” (10). The keywords were primarily categorized into three clusters, with distinct colors denoting various categories. The red cluster, with eight keywords, mostly depicted the pathophysiology and prevention of fibrosis, with key terms like “inflammation,” “epidural fibrosis,” “laminectomy,” and “prevention,” among others. The green cluster, with six terms, predominantly represented anti-fibrotic agents, with principal keywords including “adcon-l,” “intra-articular injections,” “hyaluronic acid,” “adhesion,” and “scar formation.” The blue cluster, with five keywords, generally signifies an experimental model that includes “hyaluronic acid,” “reduction,” “membrane,” and “discectomy,” among others. The colors of the keywords were categorized by VOSviewer based on the year the research was published. Recent studies (highlighted in yellow on the VOSviewer overlay) emphasize keywords such as “inflammation,” “adhesion,” and “laminectomy,” suggesting a shift toward translational and regenerative approaches (Figure 7.)
DISCUSSION
This bibliometric analysis provides a structured overview of research trends on poloxamer and HA in the prevention of NRF. Although the overall number of publications remains limited, research activity has increased steadily, reflecting growing clinical awareness of postoperative adhesion as a significant complication of spinal surgery.
The quantity of publications in this domain has risen during the past two decades. Since 2000, articles have markedly advanced and shown numerous insights into the significance of preventing NRF. Turkey was the most prolific country with the highest number of publications (n=16); nevertheless, its citation count is inferior to that of China, the second most prolific country (n=13). China’s total citations (n=222) exceeded those of other countries by more than twofold, indicating that China has made significant contributions in this domain. China ranked second in total publications, with an average citation rate of 18.5, surpassing that of other countries. Consequently, a greater number of high-quality papers are indeed written in China.
Different journals address distinct fields of publication. The bibliometric approach identifies the most effective journals and significant publications within a specific field, thereby outlining the developmental trajectory for researchers in that area. Excluding journals that published only a single article, the analysis reveals that five journals are associated with the field of neurosurgery, while two are linked to orthopedics. This suggests that NRF was the central point of various research disciplines. The Journal of Orthopedic Surgery and Research recorded the highest impact factor at 2.8, accompanied by a citation count of 25. In contrast, the Journal of Neurosurgery-Spine had an impact factor of 2.7, with a significantly higher citation count of 68. This journal emerged as the leading choice among scholars concentrating on the prevention of NRF through the use of poloxamer and HA.
The exact mechanism underlying postoperative peridural adhesion remains ambiguous. LaRocca et al., reported that the formation of a membrane known as the laminectomy membrane, resulting from epidural and peridural adhesion, is attributed to the posterior invasion of fibroblasts originating from the erector spinal muscles.16 Songer et al., have suggested that epidural fibrosis develops due to the substitution of epidural fat with hematoma. The absorption of the hematoma subsequently results in the formation of granulation tissues, which evolve into dense fibrotic tissue over time.17 Nonetheless, irrespective of the precise mechanism underlying the formation of postoperative peridural adhesions, it appears that preventing or restricting fibroblast proliferation from interacting with the exposed dura during the early healing phase is a crucial element in mitigating adhesion formation.17–19
Many earlier studies have investigated the effectiveness of several anti-adhesive agents for the prevention of NRF and adhesion by means of experimental animal models.3,20–25 However, the results were not that satisfying, the adhesion following laminectomy is still one of significant complications. A notable hydrogel that has the potential to address these limitations is the FDA-approved poloxamer gel.6–9 They can be administered via injection, presenting a treatment method that is less invasive in comparison to implantable hydrogels.26,27 Poloxamer gels are structurally crosslinked and organize into hydrogels in situ, creating sphere-like micelles and dehydrating the core above a particular temperature, making them temperature-responsive.28,29 Poloxamer hydrogels exhibit remarkable biocompatibility and quick responsiveness for controlled drug delivery.28–30 Notwithstanding their potential, poloxamer hydrogels swiftly discharge substantial hydrophilic macromolecules,27 partly due to its fast degradation under physiological circumstances.28,31 This rapid erosion is due to their low molecular weight, robustness and fluid-like properties, resulting in surged and rapid cumulative releases.32,33 Hyaluronic acid has been incorporated into the structure of the hydrogel to decrease the rate of hydrogel erosion and to delay the release of drugs.34–36 Additionally, the incorporation of hyaluronic acid into poloxamer hydrogels can contribute to the mucoadhesive properties of the hydrogels.34,37 Hyaluronic acid possesses inflammation-modulating properties, advantageous after spinal cord injuries.38–41 Rongshuai Yang et al., identified that the combination of poloxamer and HA (PHA) hydrogel exhibited a positive effect on collagen biosynthesis.42 The reduction in the expression levels of matrix metalloproteinases (MMP)-9 and MMP-13, along with tissue inhibitor metalloproteinases (TIMP)-1, serves as a clear demonstration of this phenomenon. The remodeling of connective tissues is governed by matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) in both normal physiological and pathological conditions. The MMPs are crucial in the regulation of extracellular matrix (ECM) turnover within fibrotic tissues.43,44 The deposition of newly synthesized collagen is facilitated by the degradation of normal ECM components in the early phases of fibrosis during repair and scar formation. This is achieved through the mediation of cell migration, leukocyte activation, antimicrobial defense mechanisms, and inflammatory reactions.44–49
The most often occurring terms were “epidural fibrosis” (32), “laminectomy” (24), “peridural fibrosis” (17), “prevention” (16), “surgery” (13), “membrane” (11), “adhesion” (10), and “scar formation” (10). Furthermore, we identified that “adhesion,” “inflammation,” and “laminectomy” have emerged as prominent study focal points in recent years. These data suggest that clinicians have lately acknowledged the danger of NRF and adhesion following laminectomy.
This research had many shortcomings. The studied data were solely obtained from the WoSCC database, which, although extremely dependable for scientometric investigations, is limited in breadth. Secondly, possible bias may emerge from the dependence on software tools for data extraction. Finally, articles from 2025 were omitted from our study due to inadequate data throughout our database search.
LIMITATION
This study was limited to publications indexed in the Web of Science Core Collection, which may exclude relevant studies from other databases. Bibliometric analysis evaluates publication patterns and research networks rather than experimental quality, and citation-based metrics may be influenced by database coverage and time-dependent bias.
CONCLUSION
This bibliometric analysis demonstrates increasing research interest in the use of poloxamer and hyaluronic acid for the prevention of nerve root fibrosis. Current trends highlight a shift toward inflammation modulation and biomaterial optimization, supporting further translational and clinical research to improve postoperative outcomes following spinal surgery.
Author contributions
Each author work equally
Financial support
No funding
Acknowledgement
No
Conflicts of interest statement
No

_showing_progressive_growth_with_a_peak_in_2016_and_st.png)
_co-authorship_network_showing_clustered_collaborations._(b)_author_co-citation_map_hig.png)
_showing_progressive_growth_with_a_peak_in_2016_and_st.png)
_co-authorship_network_showing_clustered_collaborations._(b)_author_co-citation_map_hig.png)